The donut hole is a common term in health insurance discussions. It mainly applies to Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage. Many beneficiaries feel confused when entering the donut hole stage. This coverage gap can increase out of pocket medication costs temporarily. Understanding the medicare coverage gap helps people better manage healthcare expenses. Awareness allows beneficiaries to plan prescription spending more effectively. Knowledge reduces anxiety related to unexpected medical bills.
Early education improves confidence when navigating prescription coverage changes. Clear explanations support better financial decision making for beneficiaries. Health insurance plans often include different coverage phases during a year. The medicare coverage gap represents a transition between standard and catastrophic coverage. Costs change significantly during this phase for prescription drugs. Planning ahead helps reduce financial stress during the donut hole. Education allows beneficiaries to make smarter healthcare choices.
Proactive planning ensures better budget control throughout the year. Financial literacy improves overall healthcare confidence. Understanding plan details prevents costly mistakes during transitions. Preparation supports smoother prescription management. The medicare coverage gap does not mean complete loss of prescription coverage. Instead, it changes how costs are shared between members and plans.
Table of Contents
Understanding Medicare Part D Coverage Phases
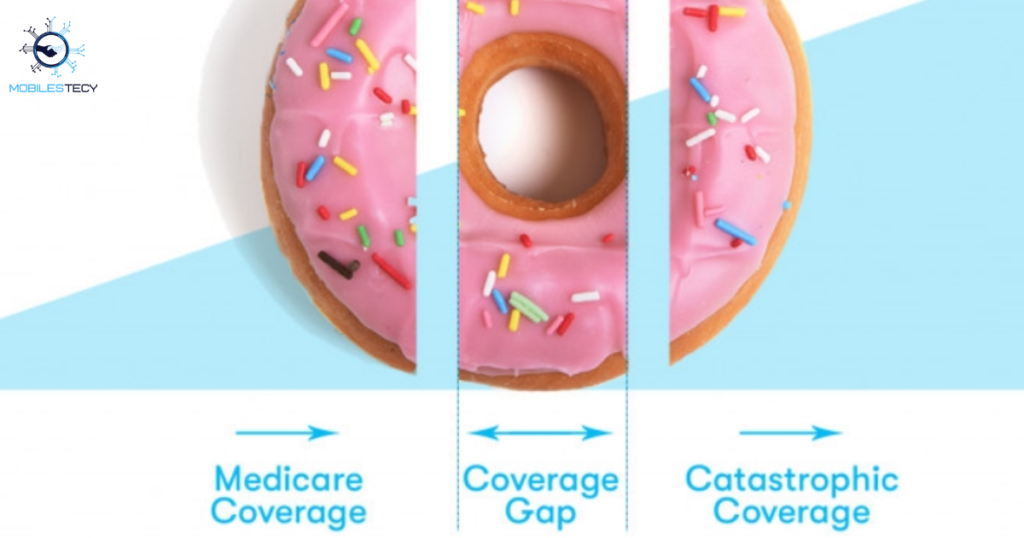
Medicare Part D provides prescription drug coverage through private insurance plans. Coverage follows specific stages that reset every calendar year. Each stage affects how much beneficiaries pay for medications. The donut hole occurs after initial coverage limits are reached. Knowing these stages helps members track prescription spending accurately. Tracking expenses helps prevent unexpected coverage transitions.
Awareness supports better medication planning. Careful monitoring reduces financial uncertainty. Understanding stages encourages proactive healthcare decisions. The first stage is the deductible phase of coverage. During this phase, beneficiaries pay full medication costs. Once the deductible is met, initial coverage begins. This stage offers predictable copayments or coinsurance. Most beneficiaries spend significant time in this phase.
Costs remain more manageable during this period. Understanding deductibles improves budgeting accuracy. Early preparation minimizes financial pressure. Clear expectations help manage healthcare costs. After initial coverage, beneficiaries may enter the medicare coverage gap. This happens when total drug costs reach a specific threshold. During the donut hole, cost sharing increases temporarily. Members pay a percentage of medication costs.
Ways to Reduce Medicare Coverage Gap Impact
Choosing the right Medicare Part D plan is essential. Plans differ in coverage, formularies, and cost sharing. Selecting appropriate coverage reduces donut hole expenses. Annual plan reviews are highly recommended. Comparing plans helps identify cost saving opportunities. Informed choices lower long term expenses.
Using generic medications helps delay medicare coverage gap entry. Generics cost less than brand name alternatives. Doctors can suggest effective lower cost substitutions. This strategy saves money throughout the year. Consistent use of generics reduces prescription spending. Savings accumulate over time.
What Happens During the Medicare Coverage Gap

The donut hole is also called the Medicare Part D coverage gap. It represents reduced coverage for prescription medications. Beneficiaries pay higher percentages for drugs during this phase. Both brand name and generic drugs are affected. Costs may feel sudden without proper preparation. Awareness minimizes financial shock. Planning ensures smoother transitions. Understanding rules reduces confusion.
Preparedness improves financial stability. Healthcare reforms have significantly reduced medicare coverage gap expenses. Today, beneficiaries generally pay about twenty five percent costs. Manufacturer discounts help reduce brand name drug expenses. These discounts count toward exiting the donut hole faster. This makes the coverage gap more manageable. Discounts play an important financial role. Savings help beneficiaries progress quicker.
Policy changes improved affordability. Reforms increased coverage fairness. The medicare coverage gap continues until out of pocket limits are reached. Once reached, catastrophic coverage begins automatically. Prescription costs decrease significantly during catastrophic coverage. This protection lasts for the remainder of the year. Coverage resets again at the start of next year. Annual resets require renewed planning. Budget cycles restart yearly.
Extra Help and Assistance Programs
The Medicare Extra Help program assists low income beneficiaries. It significantly reduces prescription drug costs. Some participants never experience the donut hole. Eligibility depends on income and resource limits. This program provides substantial financial relief. Applications should be completed early.
State pharmaceutical assistance programs also provide support. These programs vary by state and eligibility criteria. They help cover prescription costs during coverage gaps. Applying early ensures timely assistance. State resources complement federal programs. Local guidance improves enrollment success..
Who Is Most Affected by the Medicare Coverage Gap

People with chronic illnesses often reach the donut hole quickly. They require multiple or expensive prescription medications. Brand name drugs accelerate entry into the coverage gap. Specialty medications increase overall prescription spending rapidly. These individuals must plan carefully for costs. Monitoring expenses becomes extremely important. Assistance programs provide relief. Preventive care reduces medication reliance. Informed choices lower risk.
Early planning reduces financial burden. Support ensures continuity of care. Seniors living on fixed incomes feel donut hole effects strongly. Even moderate cost increases can strain monthly budgets. Unexpected prescription expenses create financial stress. Budgeting becomes essential during the medicare coverage gap period. Support programs can help reduce burden. Financial counseling offers additional support.
Planning improves peace of mind. Education empowers better financial decisions. Prepared seniors manage expenses better. Some beneficiaries never enter the donut hole stage. Those using few low cost generic medications often avoid it. Medication choices influence coverage phase progression significantly. Regular plan reviews help predict medicare coverage gap entry. Understanding usage patterns improves financial planning. Tracking medications supports smarter decisions. Awareness promotes cost control.
Common Medicare Coverage Gap Misconceptions
Many believe the donut hole no longer exists entirely. In reality, the coverage gap still remains. Costs are reduced but not eliminated completely. Understanding facts prevents misinformation. Education dispels common myths. Accurate knowledge improves decision making. Clarification reduces anxiety. Reliable sources matter greatly.
Some think medicare coverage gap means no coverage at all. Coverage continues with higher cost sharing. Beneficiaries still receive plan and manufacturer support. This distinction is very important. Misunderstanding can cause unnecessary fear. Correct information builds confidence. Awareness improves financial readiness.
- The donut hole applies mainly to Medicare Part D prescription coverage.
- It begins after reaching initial prescription spending limits.
- Beneficiaries pay higher drug costs temporarily during this phase.
- Healthcare reforms have reduced donut hole financial burden.
- Planning helps manage prescription costs effectively.
Faq’s
What is the medicare coverage gap in health insurance?
It is a temporary coverage gap in Medicare Part D prescription plans. Understanding it helps manage medication costs.
Does the donut hole mean no prescription coverage?
No, coverage continues with higher cost sharing during this stage. Financial assistance still exists.
Who enters the donut hole fastest?
People taking expensive or multiple medications enter faster. Chronic conditions increase risk.
How can I avoid the medicare coverage gap?
Using generics and choosing suitable plans may delay entry. Annual reviews are helpful.
Does catastrophic coverage end the donut hole?
Yes, costs drop significantly after reaching catastrophic coverage. Protection lasts remainder of year.
Conclusion
The donut hole remains an important concept in health insurance education. It affects how Medicare beneficiaries pay for prescriptions. Understanding coverage stages helps avoid financial surprises. Preparation reduces stress during higher cost periods. Knowledge leads to better healthcare planning. Awareness empowers proactive decisions. Confidence improves healthcare experiences.
Education promotes financial security. Informed patients achieve better outcomes. Healthcare reforms have improved medicare coverage gap affordability significantly. Beneficiaries now pay less than in previous years. Still, costs can impact those with complex medical needs. Support programs offer valuable financial relief. Utilizing resources improves outcomes. Assistance ensures medication access. Planning remains essential. Community support strengthens resilience.
Ultimately, understanding the donut hole empowers smarter decisions. Planning medications and reviewing plans annually is essential. Beneficiaries benefit from proactive healthcare management. Informed choices reduce unnecessary prescription expenses. Education ensures confidence throughout the coverage year. Knowledge protects financial stability. Prepared members achieve better outcomes.
Read more latest Articles on Mobilestecy.com








