Tropical diseases have plagued human populations for centuries across diverse regions. They thrive in warm, humid climates where sanitation and healthcare are scarce. Millions of people suffer annually, facing poverty, disability, and lifelong challenges. The burden is especially heavy in developing countries with limited resources. Technology has played a crucial role in tackling these persistent threats.
Lymphatic filariasis, a major tropical disease, impacts millions across the globe. It is caused by parasitic worms transmitted through mosquito bites repeatedly. The condition leads to severe swelling, disability, and social discrimination. Communities living with the disease experience economic losses and limited opportunities. Traditional methods failed, demanding stronger innovations to break cycles of infection.
Modern technology introduced new solutions that transformed tropical disease management dramatically. Pharmaceutical breakthroughs, genomic research, and digital tools reshaped medical strategies. Collaboration between scientists, governments, and communities fueled remarkable progress. Once-ignored diseases became treatable and increasingly preventable across multiple regions.
The Burden of Tropical Diseases

Tropical diseases disproportionately affect low-income populations in developing nations. They spread through poor sanitation, lack of healthcare, and insect vectors. This creates cycles of poverty, ill health, and limited opportunities. Communities struggle with disability, stigma, and social isolation for years. The economicburden further deepens inequality across vulnerable global populations.
Lymphatic filariasis, caused by parasitic worms, affects millions globally. The disease leads to chronic swelling, disability, and lifelong suffering. Patients face severe discrimination, making employment and relationships difficult daily. Children often leave school early due to painful physical limitations. Entire families bear the burden of caregiving responsibilities and poverty.
Traditional treatments failed to fully cure or stop transmission effectively. Medicines only reduced symptoms, leaving parasites inside the human body. Vector control strategies showed inconsistent results across various tropical regions. Communities remained trapped in cycles of infection and recurring illness. A new technological approach was urgently needed for meaningful progress.
Pharmaceutical Breakthroughs in Tropical Disease Control
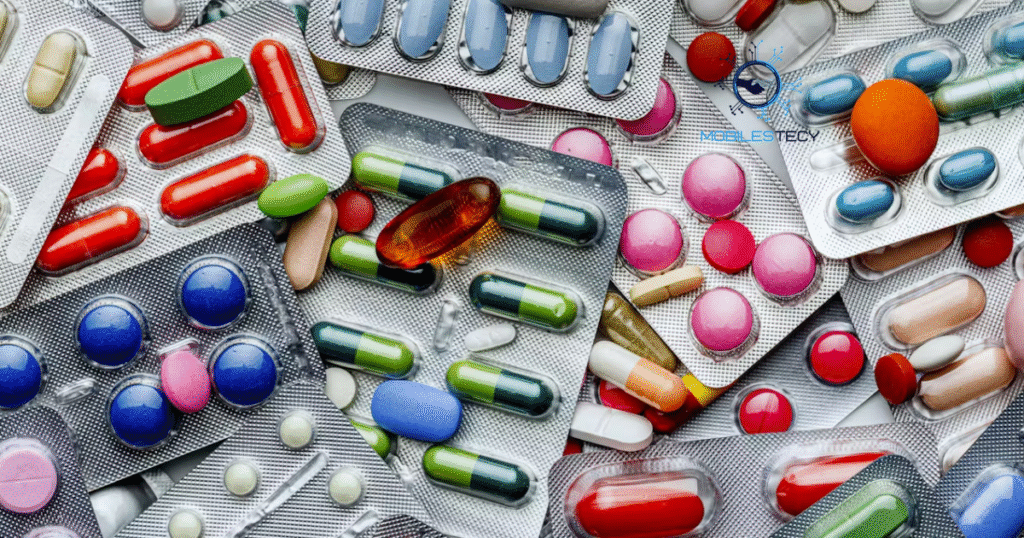
The development of antiparasitic drugs changed the fight against filariasis. Ivermectin, albendazole, and diethylcarbamazine became central treatment innovations worldwide. These medicines targeted parasites effectively, reducing infection and stopping further transmission. Millions of patients received long-term relief and protection from reinfection. Pharmaceutical advancements brought hope to communities plagued by tropical diseases.
Combination therapy emerged as a powerful innovation for eliminating infections. WHO recommended mass drug administration using these medicines across endemic countries. Entire villages received treatment simultaneously, cutting disease prevalence significantly over time. This strategy protected vulnerable populations while reducing overall transmission rates. Gradually, progress shifted toward regional elimination of lymphatic filariasis.
Drug distribution programs relied heavily on international support and partnerships. Nonprofit organizations worked with pharmaceutical companies for large-scale donations. Local health workers ensured medicines reached remote, underserved rural communities. Community trust and education were vital in ensuring program acceptance. Together, these collaborations made elimination campaigns achievable and sustainable.
Community Participation in Disease Elimination
Community involvement proved critical for the success of medical programs. Local volunteers supported health workers by educating neighbors about treatments. Trust built within communities increased acceptance of large-scale drug distribution. Without community engagement, elimination campaigns would fail to achieve goals.
Community-based leadership networks were established in villages to raise awareness and encourage consistent involvement in elimination efforts. Culturally sensitive educational approaches ensured that messages aligned with local traditions, beliefs, and social practices.
The Role of Technology in Disease Elimination
Technology played an increasingly vital role beyond medical treatment by improving surveillance, monitoring, and distribution systems. Digital mapping tools allowed health teams to identify outbreak zones and prioritize high-risk areas. Mobile data collection enabled health workers to report cases instantly from the field, improving the speed and accuracy of decision-making. These tools enhanced resource planning and enabled more precise and effective intervention strategies.
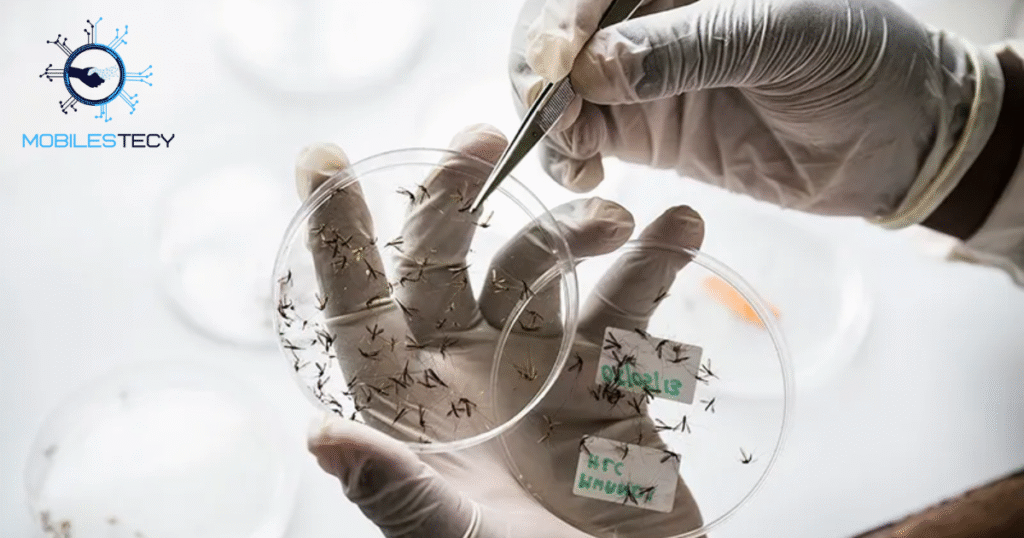
Advances in genetic research provided scientists with deeper insights into parasites and disease-carrying mosquitoes. By analyzing parasite DNA, researchers discovered biological vulnerabilities that could be targeted through new medications and vaccines. Sequencing the genomes of mosquito vectors also supported the creation of more precise and innovative vector control methods. These breakthroughs brought global disease elimination goals closer to reality through scientific precision and improved treatment strategies.
Collaboration among governments, research institutions, and nonprofit organizations further accelerated technological progress. Artificial Intelligence systems predicted outbreaks by analyzing climate trends, population movement, and health patterns. Drones were deployed to deliver essential medicines to rural and geographically isolated communities. Public awareness campaigns leveraged digital platforms to educate and motivate participation on a wide scale.
Education and Awareness Campaigns
Awareness campaigns educated populations about prevention and treatment importance. Schools, religious centers, and social groups became key communication platforms. Radio broadcasts and posters spread information widely in rural environments. These strategies ensured people understood disease risks and possible solutions.
Education empowered individuals to take responsibility for personal health. Informed citizens recognized mosquito control and hygiene as protective measures. This knowledge reduced reinfection risks and promoted healthier living standards. Awareness campaigns played a lasting role in disease prevention.
Future Innovations in Tropical Disease Control
Research continues developing vaccines to fully eradicate tropical parasitic infections. Scientists work tirelessly to enhance effectiveness and accessibility of new treatments. Artificial intelligence predicts outbreaks by analyzing climate and population data. Innovations in biotechnology offer powerful solutions for disease elimination globally.
Future advancements will combine medicine, digital tools, and biotechnology seamlessly. Drone networks and telemedicine will expand healthcare access to remote regions. Cross-border collaborations will accelerate research and resource distribution worldwide. Technology ensures progress toward a disease-free future becomes increasingly achievable.
- Pharmaceutical breakthroughs introduced combination therapy, reducing infection and transmission significantly.
- Mass drug administration programs protected millions across rural, underserved communities worldwide.
- Digital technologies improved outbreak monitoring and enhanced data-driven health strategies.
- Genomic research revealed parasite vulnerabilities, accelerating vaccine and drug development.
- Global collaborations strengthened elimination efforts through funding, logistics, and awareness.
Faq’s
Which technological advancement helped cure lymphatic filariasis successfully worldwide?
Combination therapy with ivermectin, albendazole, and diethylcarbamazine proved effective.
How do digital health tools support tropical disease elimination programs today?
They track outbreaks, monitor progress, and ensure efficient treatment distribution.
What role does genomic research play in fighting tropical diseases?
It identifies parasite weaknesses and accelerates vaccine and drug development.
Why is community participation essential in mass drug administration campaigns?
Community trust ensures acceptance, compliance, and effective program implementation.
How can future technology improve tropical disease elimination worldwide?
Biotechnology, AI, and telemedicine will transform prevention and treatment methods.
Conclusion
Tropical diseases once caused devastating consequences across vulnerable global communities. Technological advancements transformed public health strategies, offering hope and resilience. Pharmaceutical breakthroughs, genomic research, and digital tools redefined elimination efforts. Communities witnessed progress once considered impossible within traditional healthcare approaches. These transformations demonstrated the undeniable power of science and technology.
Drug therapies reduced infection rates and enhanced mass treatment accessibility significantly. Education campaigns encouraged awareness, prevention, and acceptance of medical programs. Global partnerships strengthened resources, funding, and public health program delivery. Technology extended healthcare to previously unreachable rural and isolated communities. Together, these advancements reshaped the fight against tropical diseases worldwide.
Future innovations promise a brighter future free from neglected tropical diseases. Vaccines, biotechnology, and AI-driven systems will enhance elimination strategies. Communities will gain healthier living conditions and greater socioeconomic opportunities. Global health equity will progress as science advances medical solutions. The journey continues toward permanently curing tropical diseases worldwide.
Read more latest Articles on Mobilestecy.com








