Intrauterine insemination, commonly referred to as IUI, is a popular fertility treatment used by couples and individuals struggling with infertility. It involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus around the time of ovulation to increase the chances of conception. While IUI is less invasive and less expensive than procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF), many patients worry about whether insurance covers it. Understanding coverage options, costs, and alternatives is essential for anyone considering this treatment.
Infertility affects millions of couples worldwide, and fertility treatments can be emotionally and financially taxing. The cost of an Intrauterine cycle varies depending on several factors, including medications, monitoring, and clinic fees. Without insurance coverage, patients may face thousands of dollars in out-of-pocket expenses. Insurance coverage for fertility treatments differs widely between states, insurance companies, and even between individual policies, making it crucial to research and plan ahead.
Patients often find themselves confused by the complexity of insurance policies related to fertility. Many plans specifically exclude assisted reproductive technologies, while others offer partial coverage. Determining whether your policy covers IUI requires examining the policy language, understanding state mandates, and sometimes speaking directly with the insurer. Patients who proactively explore these details can significantly reduce financial stress while pursuing fertility treatment.
Table of Contents
Understanding IUI and How It Works
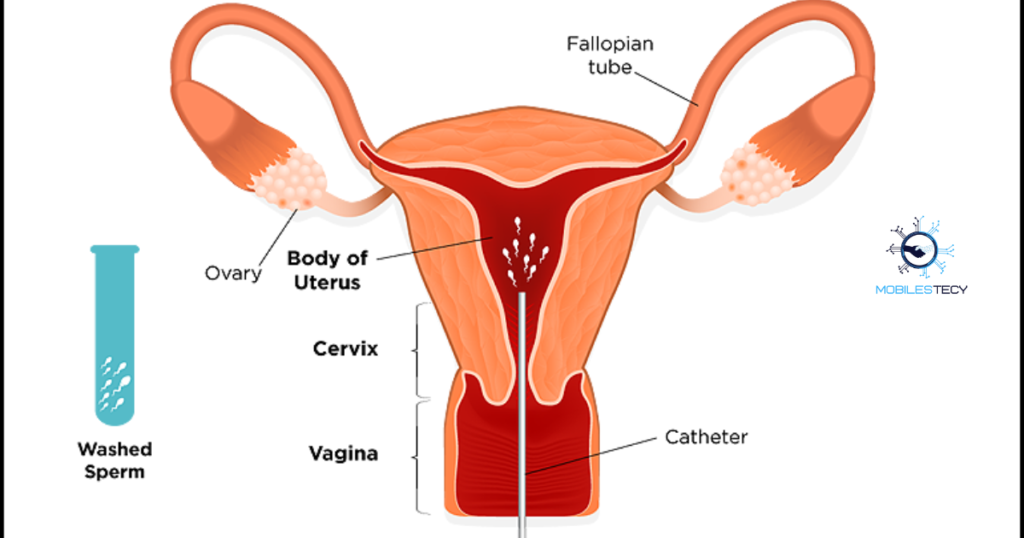
IUI is one of the simplest fertility treatments available, often recommended for couples with mild male factor infertility, unexplained infertility, or ovulation issues. The process involves monitoring ovulation, preparing sperm in a laboratory to increase its quality, and then inserting it into the uterus using a thin catheter. By placing sperm directly into the uterus, IUI reduces the distance sperm must travel, increasing the chances of fertilization.
The success rate of IUI varies depending on factors such as age, fertility diagnosis, and whether fertility medications are used. On average, IUI has a success rate of 10–20% per cycle for women under 35. For women over 40, the success rate drops significantly, often requiring multiple cycles or alternative treatments like IVF. Because of these variables, insurance coverage can play a major role in patient decisions.
IUI typically involves several components: fertility medications, monitoring appointments, lab work, and the insemination procedure itself. Fertility medications, like Clomid or gonadotropins, stimulate ovulation and can improve the chances of conception. Monitoring appointments include ultrasounds and blood tests to track follicle development and hormone levels. Each of these components can carry separate costs, some of which may or may not be covered by insurance.
Alternatives When Insurance Doesn’t Cover Intrauterine
Patients whose insurance does not cover IUI have several options. Fertility discount programs or bundled treatment packages from clinics may reduce costs. Some clinics offer shared-risk programs where patients pay upfront and are partially reimbursed if treatment fails. Nonprofit organizations and grants also exist to support patients struggling with infertility expenses.
Another alternative is to explore Medicaid coverage or state-specific programs for infertility treatment. While coverage is limited, some states provide support for diagnostic procedures or fertility preservation. Patients can also consult fertility navigators or financial counselors at clinics to identify affordable strategies and maximize existing insurance benefits.
Insurance Coverage for IUI
Coverage for IUI depends heavily on the type of insurance policy you have. Some insurance plans explicitly cover fertility treatments, while many others exclude assisted reproductive technologies altogether. Standard health insurance policies often cover diagnostic tests, consultations, and basic procedures, but not the actual insemination. Patients must carefully review their benefits and any fertility-specific riders included in their policy.
State mandates also affect coverage for fertility treatments. In certain states like Massachusetts, Illinois, and New Jersey, insurance companies are required to cover or offer coverage for infertility treatments, including IUI. However, even in mandated states, coverage may have limitations regarding the number of cycles, age restrictions, or medical necessity requirements. Patients living in states without mandates may find it more challenging to secure coverage.
Some insurance plans cover fertility medications associated with IUI, while others do not. Fertility medications can cost anywhere from $50 to over $500 per cycle, depending on the type and dosage. Patients should check whether their plan covers prescriptions, whether prior authorization is required, and if there are restrictions on brand versus generic medications. Coverage for medications can significantly reduce out-of-pocket costs.
Components Often Covered
While IUI itself may not be fully covered, insurance often covers related diagnostic tests. Blood work, semen analysis, ovulation monitoring, and ultrasounds may be partially or fully covered under standard insurance benefits. This coverage helps reduce overall treatment expenses even if the insemination procedure itself requires out-of-pocket payment.
Some insurance plans may also cover complications arising from fertility treatments. For example, monitoring for multiple pregnancies, treatment for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, or other medical interventions may be included. Patients should inquire about these potential benefits when confirming coverage.
Costs of IUI Without Insurance

The cost of an IUI cycle without insurance can range significantly. A basic cycle may cost between $300 and $1,000 for the procedure alone. Fertility medications add an additional $50–$500 per cycle, depending on the type used. Monitoring, ultrasounds, and lab work may add another $200–$500. Overall, the total cost per IUI cycle without insurance can range from $500 to $2,000.
Because success rates per cycle are relatively low, many patients require multiple cycles to achieve pregnancy. This can increase the total cost substantially. For couples who need three or four cycles, expenses without insurance can exceed $5,000. These costs do not include additional services such as genetic testing or consultations with specialists. Employers’ group health plans may also have exclusions or annual maximums.
Patients should also account for indirect costs, such as travel to fertility clinics, time off work, and emotional support services. Fertility treatment is often an investment not only financially but also emotionally and physically, making insurance coverage a critical consideration for many couples. Coverage depends on patient age, medical diagnosis, and prior treatments. Some insurance plans require patients to try less expensive treatments before covering IUI.
Tips for Navigating Insurance
Confirming coverage before starting treatment is critical. Ask your insurance company about covered procedures, medications, and any prior authorization requirements. Keep detailed records of all appointments, prescriptions, and lab tests to simplify claims. Speak with your fertility clinic’s billing department to understand in-network vs. out-of-network costs.
Patients should also compare costs across multiple clinics and consider combining financial assistance programs. Many clinics provide payment plans or sliding-scale fees for uninsured patients. Using FSAs or HSAs to cover out-of-pocket costs can further reduce financial burden. Being informed and prepared ensures that couples can pursue IUI treatment.
- IUI coverage depends heavily on insurance type and state fertility mandates.
- Fertility medications, monitoring, and lab work may sometimes be covered separately.
- Costs without insurance range from five hundred to two thousand dollars.
- Multiple cycles often increase overall expenses significantly for patients pursuing IUI.
- Financial planning, discount programs, and FSAs can help reduce out-of-pocket costs.
Faq’s
Does insurance usually cover IUI treatment fully?
Most standard insurance plans do not cover the IUI procedure fully.
Are fertility medications covered by insurance?
Coverage varies; some plans cover medications while others require out-of-pocket payment.
What states mandate insurance coverage for fertility treatments?
States like Massachusetts, Illinois, and New Jersey require some fertility treatment coverage.
Can I use FSA or HSA for IUI costs?
Yes, FSA and HSA accounts can pay for IUI procedures and medications pre-tax.
How many cycles of IUI do patients usually need?
Success rates are 10–20% per cycle, often requiring multiple cycles for conception.
Conclusion
IUI is a widely used fertility treatment that can help many couples conceive. Insurance coverage for IUI varies greatly depending on the plan, state mandates, and individual patient circumstances. Even if the procedure is not fully covered, related costs like diagnostic tests and medications may receive partial coverage. Understanding the policy language and consulting both the insurance provider and fertility clinic is essential.
The cost of IUI without insurance can be substantial, ranging from five hundred to two thousand dollars per cycle. Many patients require multiple cycles, further increasing expenses. Financial planning, clinic discount programs, and pre-tax accounts like FSA or HSA can significantly reduce out-of-pocket costs. Patients who proactively explore coverage and financial strategies can manage expenses effectively while pursuing their fertility goals.
Navigating insurance for fertility treatment requires careful research and planning. Confirming coverage before starting treatment, understanding state mandates, and consulting clinic billing experts reduces stress and unexpected costs. Ultimately, being informed empowers patients to make the best decisions for their reproductive health while minimizing financial burden. Be proactive in understanding state mandates and plan exclusions to avoid unexpected expenses.
Read more latest Articles on Mobilestecy.com








