Cataracts develop when the eye’s natural lens becomes cloudy over time. They gradually reduce vision clarity, making daily tasks difficult and dangerous. Cataract surgery is the most effective treatment to restore clear vision. Many patients wonder whether health insurance will help cover the costs. Understanding coverage options prevents unexpected bills and ensures proper financial planning. Knowing your policy helps make informed decisions about scheduling surgery effectively.
Insurance coverage often depends on the type of plan and medical necessity. Most insurers cover surgery if cataracts impair vision significantly and daily life. Premium lenses like multifocal or toric may require additional out-of-pocket payments. Documentation from an ophthalmologist may be required for approval by the insurer. Deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance affect total out-of-pocket costs for patients. Proper planning ensures the procedure is both medically necessary and affordable.
Patients should contact their insurance provider before scheduling cataract surgery. Reviewing your policy helps clarify which services and lenses are covered. Understanding coverage avoids delays, denied claims, and unnecessary financial stress later. Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance handle coverage differently depending on eligibility. Supplemental insurance may assist with out-of-pocket costs for elective lens options. Careful coordination between surgeon and insurer ensures smooth scheduling and payment process.
Table of Contents
Understanding Cataracts and Their Effects
Cataracts affect millions of people worldwide, mostly older adults over sixty years. They cause blurry vision, glare sensitivity, and difficulties with nighttime driving. If left untreated, cataracts can significantly impair daily activities and independence. Surgery is recommended when vision loss affects tasks like reading or driving. Removing the cloudy lens restores clarity, improving safety and quality of life. Early diagnosis allows patients to plan for surgery and confirm insurance coverage.
Several factors increase cataract risk, including aging, diabetes, and smoking habits. Prolonged sun exposure and certain medications may accelerate cataract development over time. Family history of cataracts also plays an important role in eye health risk. Patients should consult an ophthalmologist if they notice gradual vision changes. Eye examinations determine severity and suitability for cataract surgery effectively and safely. Timely intervention can prevent complications and ensure better surgical outcomes for patients.
Modern cataract surgery is safe, effective, and widely performed on outpatients. Techniques like phacoemulsification and laser-assisted surgery reduce recovery time significantly. Most patients experience improved vision within days after the procedure is completed. Surgery involves replacing the natural lens with an artificial intraocular lens carefully. Proper pre-operative preparation helps patients understand costs, insurance, and medical requirements. Insurance coverage is essential to manage expenses and maximize benefits for patients.
Types of Insurance Covering Cataract Surgery
Private health insurance often covers cataract surgery if medically necessary and documented. Coverage usually includes pre-operative evaluation, the procedure, and post-operative care. Premium lens options may require additional payments beyond standard coverage limits. Medicare Part B in the United States covers standard lens cataract surgery.
Medicaid coverage varies by state but usually covers medically necessary cataract surgery. Some states require prior authorization or proof of functional vision impairment. Patients should contact their state Medicaid office to confirm coverage before surgery. Veterans may access VA benefits, covering surgery fully for eligible beneficiaries.
Determining Medical Necessity for Insurance Approval
Insurance covers cataract surgery only when deemed medically necessary by a physician. Medical necessity is proven by impaired vision affecting daily living activities. Eye exams, visual acuity tests, and documentation are required for approval. Functional limitations, such as trouble driving or reading, support medical necessity claims. Insurance companies review documentation carefully before granting surgery coverage or pre-authorization. Proper medical records prevent delays and ensure timely approval for the procedure.
Patients whose cataracts do not significantly impair vision may face denied coverage. Early elective surgery with premium lenses is typically not fully reimbursed. Documentation of worsening vision helps establish urgency and eligibility for insurance approval. Prior authorization is often required to ensure the procedure meets policy criteria. Insurance providers may request evidence of previous corrective lens use and limitations. Clear communication between doctor and insurer facilitates approval and minimizes unnecessary delays.
Understanding policy coverage for pre- and post-operative care is also important. Some plans cover pre-op testing, anesthesia, and follow-up visits automatically. Others may have separate copayments or limits, which patients should clarify before scheduling. Knowing covered services prevents surprise bills and ensures financial preparedness for surgery. Patients should always verify all aspects of coverage with insurance representatives. This ensures total transparency about costs and avoids unexpected out-of-pocket expenses later.
Cost Considerations and Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Cataract surgery costs vary depending on surgeon fees, facility, and lens selection. Standard monofocal lens surgery is usually covered by insurance with minimal out-of-pocket. Laser-assisted surgery and premium lenses require additional payments not always covered by insurance.
Patients should review insurance plan limits carefully before selecting surgery type. Advanced lens options provide better vision but increase out-of-pocket expenses significantly. Professional estimates help patients budget and plan for elective lens choices appropriately. Understanding coverage versus elective services ensures realistic expectations about total financial responsibility.
Steps to Maximize Insurance Coverage
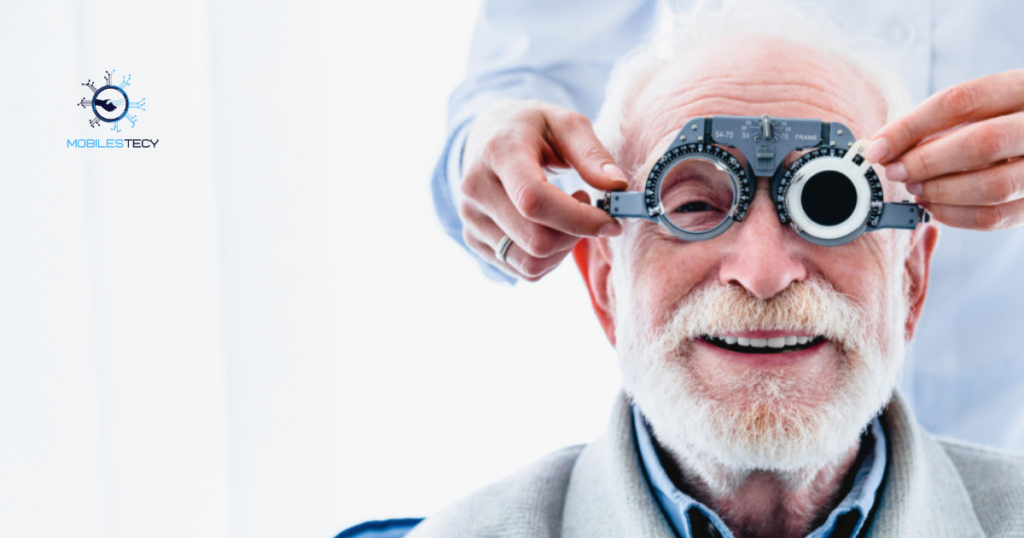

First, review your health insurance policy for coverage of cataract surgery clearly. Ensure you understand deductibles, copays, and coinsurance amounts before scheduling procedures. Confirm whether standard or premium lenses are included in your plan benefits. Second, obtain prior authorization from the insurance company before surgery whenever required. Provide documentation from your ophthalmologist confirming functional impairment due to cataracts effectively.
Third, coordinate with the surgical facility to confirm acceptance of your insurance plan. Communication between doctor, facility, and insurer is key to maximize coverage successfully. Out-of-pocket expenses can include copayments, deductibles, coinsurance, or elective lens upgrades. Careful planning ensures surgery is both medically effective and financially manageable for patients.
Patients should clarify which tests, medications, and follow-up visits are covered fully. Understanding policy limits helps avoid unexpected bills and costly surprises after surgery. Use supplemental insurance or FSAs to offset costs not covered by primary insurance. Advanced lens options may require patient payment, so plan financially for elective upgrades. Careful planning ensures surgery proceeds smoothly and avoids delays due to insurance issues.
Additional Considerations for Patients
Patients with multiple insurance policies should coordinate coverage to minimize out-of-pocket expenses. VA benefits, supplemental insurance, and FSAs can cover some costs not included by primary plans. Travel, recovery needs, or additional medical testing may require separate planning and budgeting.
Patients should discuss all options with ophthalmologists to optimize care and coverage. Knowing insurance details and potential costs ensures peace of mind and smooth recovery. Combining medical guidance with insurance knowledge ensures safety, affordability, and optimal surgical outcomes..
- Cataract surgery is usually covered if deemed medically necessary by a physician.
- Standard monofocal lenses are generally included, while premium lenses may incur costs.
- Medicare Part B and most private insurers cover medically necessary surgery effectively.
- Medicaid coverage varies by state, often requiring prior authorization and documentation.
- Out-of-pocket expenses may include deductibles, coinsurance, copayments, or elective lens upgrades.
Faq’s
Does insurance cover cataract surgery for mild vision problems?
Usually not; surgery must be medically necessary and significantly impair vision.
Are premium or multifocal lenses covered by insurance?
Generally no; patients pay the difference between standard and premium lenses.
Will Medicare pay for cataract surgery?
Yes, Medicare Part B covers medically necessary cataract surgery with standard lenses.
Does Medicaid cover cataract surgery for eligible patients?
Yes, coverage varies by state and often requires prior authorization.
Can supplemental insurance help with cataract surgery costs?
Yes, it can cover copayments, deductibles, or upgrades not covered by primary insurance.
Conclusion
Cataract surgery restores vision and improves quality of life for millions of patients. Insurance coverage depends on plan type, medical necessity, and lens selection requirements. Standard monofocal lenses are usually covered, while premium lens upgrades may require payment. Patients should review insurance policies, obtain prior authorization, and document medical necessity clearly.
Understanding medical necessity criteria is essential to avoid denied claims or delays. Patients should coordinate with ophthalmologists and insurance representatives to maximize coverage efficiently. Flexible spending accounts or supplemental insurance can reduce financial burden and cover additional costs. Clear documentation of functional impairment supports approval and smooth scheduling of surgery.
Proper insurance understanding, preventive planning, and patient-doctor communication optimize care outcomes. Knowing coverage options helps patients avoid confusion and manage expenses effectively over time. Ultimately, cataract surgery is both medically beneficial and financially manageable with careful preparation. Patients benefit from improved vision, independence, and reduced risk of accidents or injuries.
Read more latest Articles on Mobilestecy.com








