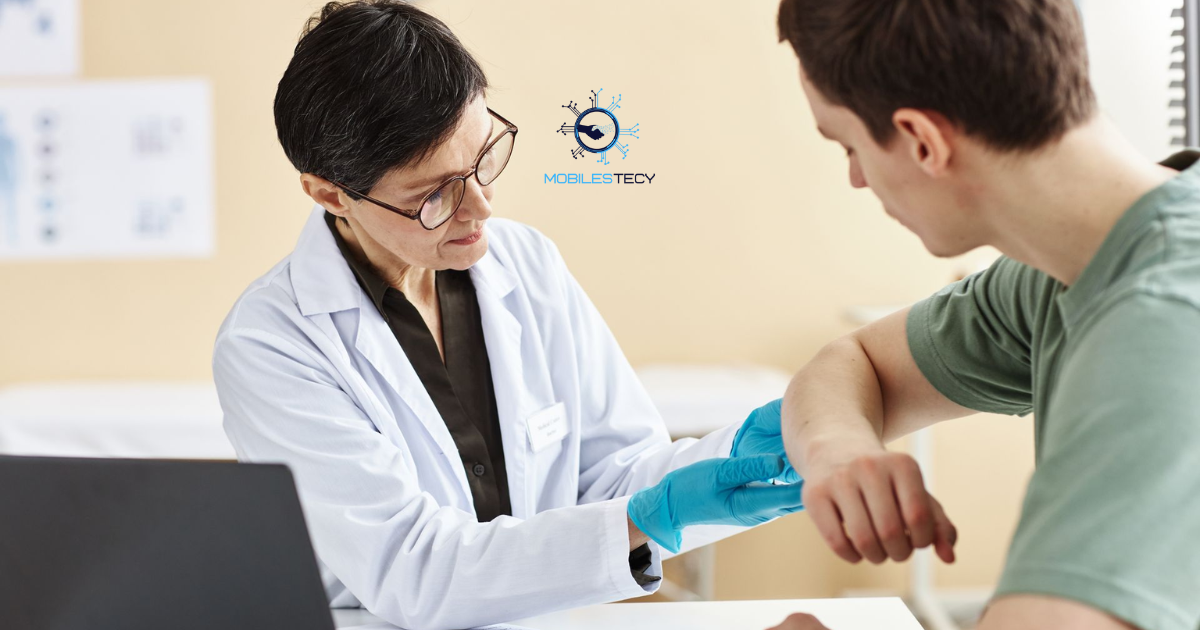
Allergy tests helps identify substances triggering uncomfortable or dangerous reactions. Many people experience ongoing symptoms without knowing the exact cause. Testing allows doctors to recommend targeted treatments and lifestyle adjustments. However, concerns about medical costs often delay proper allergy diagnosis. Insurance coverage becomes a key factor when considering allergy testing.
Allergy symptoms can affect breathing, skin health, digestion, and daily comfort. Untreated allergies may worsen over time without proper identification. Medical professionals often recommend testing for persistent or severe symptoms. Patients frequently ask whether insurance plans cover these diagnostic tests. Understanding coverage rules helps reduce unexpected healthcare expenses.
Insurance policies vary widely regarding diagnostic test coverage and requirements. Some plans fully cover allergy testing when medically necessary. Others require referrals, prior authorization, or cost sharing responsibilities. Knowing your policy details helps avoid denied claims or high bills. Proper planning makes allergy testing more affordable and accessible. Reviewing policy details and speaking to insurers can prevent surprise denials.
Table of Contents
Understanding Allergy Testing and Medical Necessity
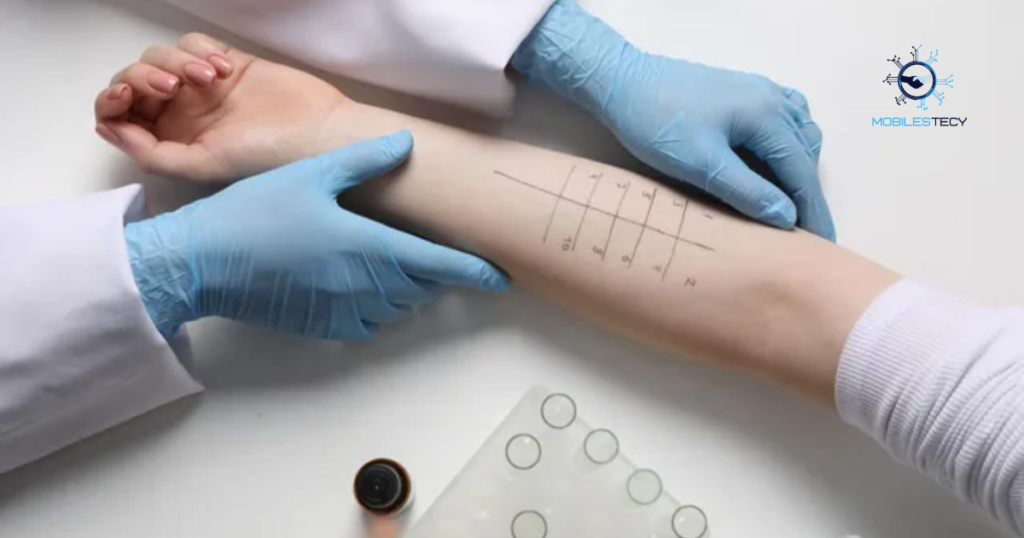
Allergy tests identify immune responses to specific allergens in the environment. Doctors order tests when symptoms persist despite standard treatment options. Testing helps confirm triggers like pollen, foods, dust mites, or pet dander. Accurate diagnosis improves treatment effectiveness and symptom management. Insurance coverage depends heavily on documented medical necessity. Identifying allergies early can prevent complications like asthma attacks or severe reactions.
Medical necessity means testing is required to diagnose or manage conditions. Insurance providers require physician justification for diagnostic procedures. Testing for curiosity or convenience is often not covered. Chronic symptoms increase the likelihood of insurance approval. Clear medical records strengthen the case for coverage approval. Providers may need to document prior treatments that were ineffective.
Severe reactions like asthma attacks or anaphylaxis justify immediate testing. Insurance companies prioritize tests preventing serious health complications. Physician referrals are often required for specialist allergy testing. Following proper medical pathways improves coverage outcomes. Skipping steps may result in denied insurance claims. Allergy documentation supports both short-term treatment and long-term health planning.
Common Types of Allergy Tests
Skin prick tests are the most commonly used allergy testing method. They provide quick results and are generally reliable. Small allergen amounts are introduced through the skin surface. Reactions indicate sensitivity to specific allergens. These tests are widely available and cost-effective for multiple allergens.
Blood tests measure allergy related antibodies in the bloodstream. They are useful when skin testing is not recommended. Certain medications or skin conditions require blood testing. Results help identify immune responses accurately. Blood testing is often used for food or drug allergy evaluation.
Insurance Coverage for Allergy Tests
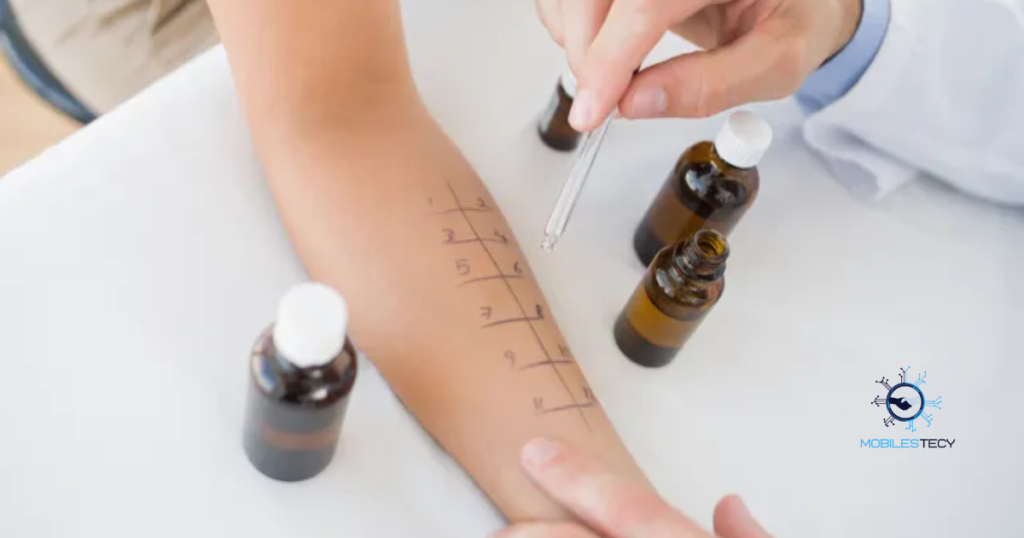

Most health insurance plans cover allergy testing under specific conditions. Coverage applies when tests are ordered by qualified healthcare providers. Patients may still pay deductibles, copayments, or coinsurance amounts. Coverage details vary depending on individual insurance plans. Confirming benefits beforehand helps avoid unexpected costs. Some insurers require documented symptoms before authorizing testing. Coverage may differ based on age, chronic conditions, or test type.
Private insurance often covers skin and blood allergy tests. Some plans limit the number of allergens tested per session. Prior authorization may be required before testing begins. Using in network providers reduces out of pocket expenses. Out of network testing may lead to partial or denied coverage. Policies may cover follow-up appointments or additional diagnostic consultations.
Government insurance programs also cover allergy testing with guidelines. Medicare covers tests deemed medically necessary by physicians. Medicaid coverage varies depending on state specific regulations. Children often receive broader diagnostic coverage benefits. Patients should verify eligibility and requirements before scheduling tests. These programs prioritize essential diagnostic procedures for chronic or severe symptoms.
How to Maximize Insurance Coverage
Patients should consult primary care doctors before allergy testing. Referrals improve insurance approval chances for specialist visits. Clear symptom documentation supports medical necessity claims. Following insurer guidelines reduces coverage denials. Prior authorization ensures insurers approve coverage before the procedure.
Verifying benefits with insurance providers is essential. Ask about prior authorization and covered test types. Confirm in network allergists and laboratories beforehand. Preparation helps minimize unexpected medical bills. Clarifying coverage for multiple allergens prevents partial claim denials.
Costs and Factors Affecting Coverage
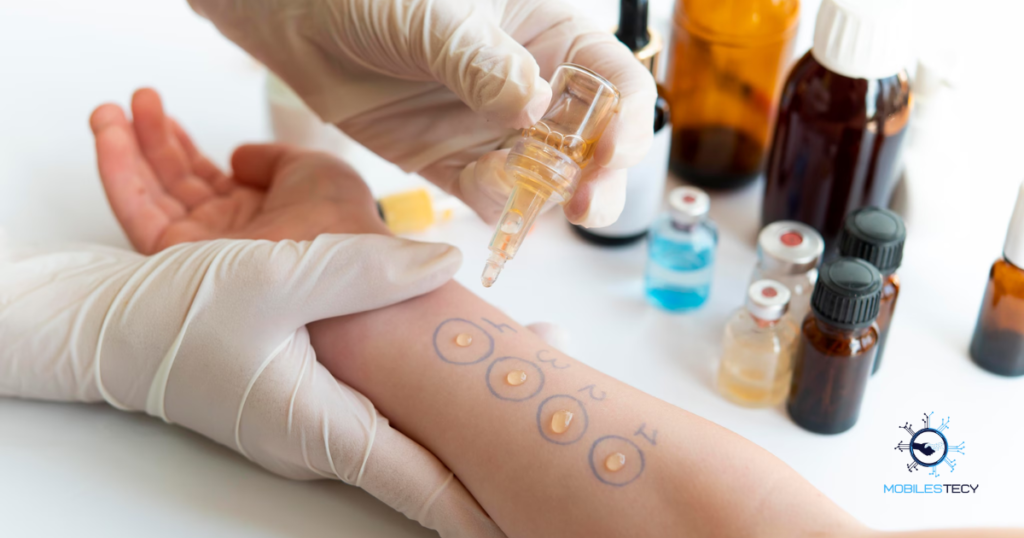
Allergy testing costs vary based on test type and provider. Skin tests are generally less expensive than blood testing panels. Extensive food allergy panels may increase total testing costs. Consultation and follow up visits add additional expenses. Insurance coverage helps significantly reduce overall costs. Out-of-pocket expenses may be higher for uninsured or out-of-network services. Patients should request cost estimates to budget properly.
Several factors influence whether insurance will cover testing. These include medical necessity, provider network status, and documentation. Deductible levels impact how much patients pay out of pocket. Policy exclusions may limit coverage for certain allergy tests. Understanding these factors helps patients plan effectively. Pre-authorization and proper documentation improve chances of full coverage.
Uninsured patients may face higher costs for allergy testing. Some clinics offer self pay discounts or payment plans. Comparing providers helps find more affordable testing options. Requesting cost estimates before testing prevents surprises. Financial planning improves access to necessary medical care. Some community or nonprofit clinics may offer reduced testing fees.
When Insurance May Not Cover Allergy Tests
Insurance may deny tests ordered without medical justification. Broad food panels without symptoms are often excluded. Testing performed by non network providers may not qualify. Lack of documentation can result in claim rejection. Certain elective or cosmetic tests are also excluded from coverage.
Some plans exclude experimental or non standard testing methods. Cosmetic or alternative allergy tests are usually not covered. Understanding exclusions prevents unnecessary expenses. Patients should review policy limitations carefully. These restrictions ensure insurance funds are used for evidence-based treatments.
- Allergy testing helps identify triggers causing chronic health symptoms.
- Insurance coverage depends on medical necessity and policy terms.
- Skin tests are commonly covered diagnostic allergy procedures.
- Out of pocket costs vary based on deductibles and copayments.
- Verifying coverage before testing prevents billing surprises.
Faq’s
Are allergy tests covered by insurance plans?
Most insurance plans cover allergy tests when medically necessary. Coverage depends on provider orders and policy details.
Do I need a referral for allergy testing?
Some insurance plans require referrals from primary care physicians. Referrals improve approval chances and coverage eligibility.
Which allergy tests are usually covered by insurance?
Skin prick and blood allergy tests are commonly covered. Coverage varies by insurer and medical justification.
Does insurance cover food allergy testing?
Food allergy testing is covered when symptoms support necessity. Routine panels without symptoms may not be covered.
What if my insurance does not cover allergy tests?
Patients may pay out of pocket or seek discounted clinics. Cost estimates help manage expenses effectively.
Conclusion
Allergy testing plays an important role in diagnosing persistent health symptoms. Insurance coverage is often available when tests are medically necessary. Understanding policy requirements helps reduce financial stress. Proper documentation improves chances of coverage approval. Planning ahead ensures smoother testing experiences. Access to insurance also encourages timely testing.
Insurance plans differ in coverage levels and cost sharing responsibilities. Patients should verify benefits before scheduling allergy tests. Choosing in network providers lowers out of pocket expenses. Following insurer guidelines prevents claim denials. Informed decisions lead to better healthcare outcomes. Careful planning ensures patients receive comprehensive and timely care. Insurance knowledge allows more proactive management of health conditions.
Allergy testing can significantly improve quality of life. Insurance coverage makes testing more affordable for many patients. Clear communication with providers and insurers is essential. With preparation, testing costs become manageable. Proactive planning supports long term health and financial stability. Testing early reduces complications and improves treatment results. Patients can avoid unnecessary medications or treatments with proper testing.
Read more latest Articles on Mobilestecy.com