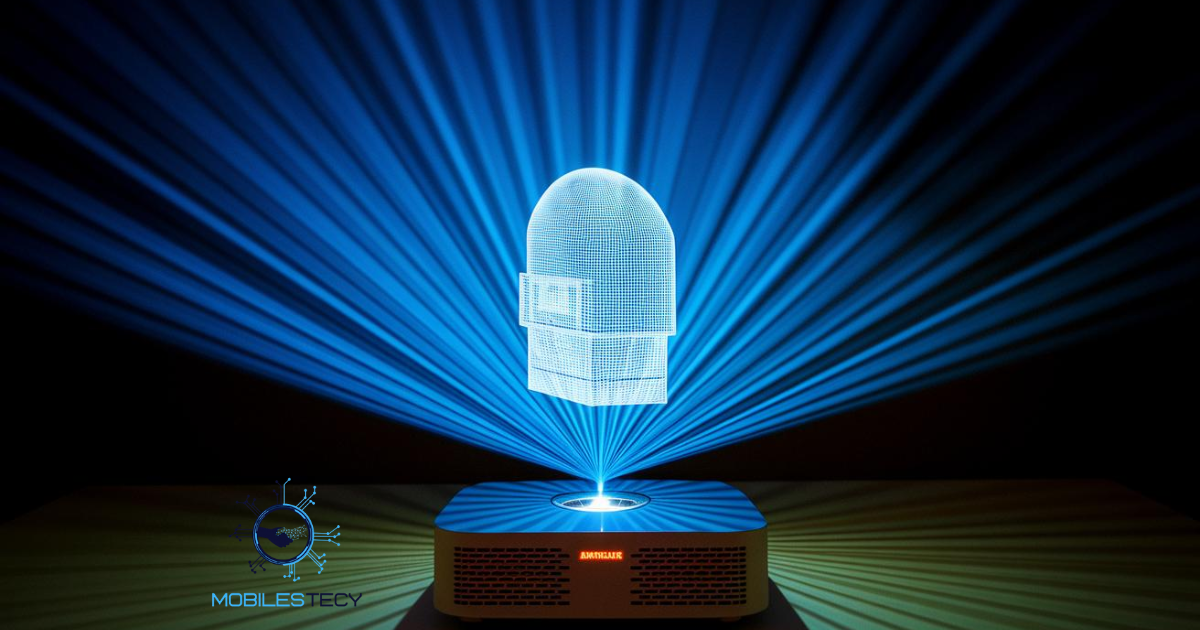
Holographic technology has shifted from imagination to reality in recent decades. It allows three-dimensional images to appear floating freely without physical screens. These holograms create immersive visual experiences for communication, entertainment, and education. Researchers continuously enhance projection clarity, depth, and realism through advanced optical methods. As innovation grows, 3D projection become more accessible across industries and global applications.
Hologram creation involves manipulating light waves to produce believable three-dimensional visuals. Modern systems use digital projectors, reflective films, and precise lighting adjustments. These components work together to display life-like images observed from multiple angles. The result is a stunning display that seems alive in open space. This technology continues evolving, making holographic presentations increasingly smooth and scalable.
Industries such as entertainment, retail, business, and education benefit greatly from holographic displays. Musicians perform virtual concerts, companies launch products, and teachers explain complex concepts visually. The captivating nature of 3D projection enhances engagement and audience attention significantly. As digital interaction rises, holographic communication may soon become mainstream. Such advancements indicate a future where virtual presence feels nearly physical.
Table of Contents
Holographic Projection Technology
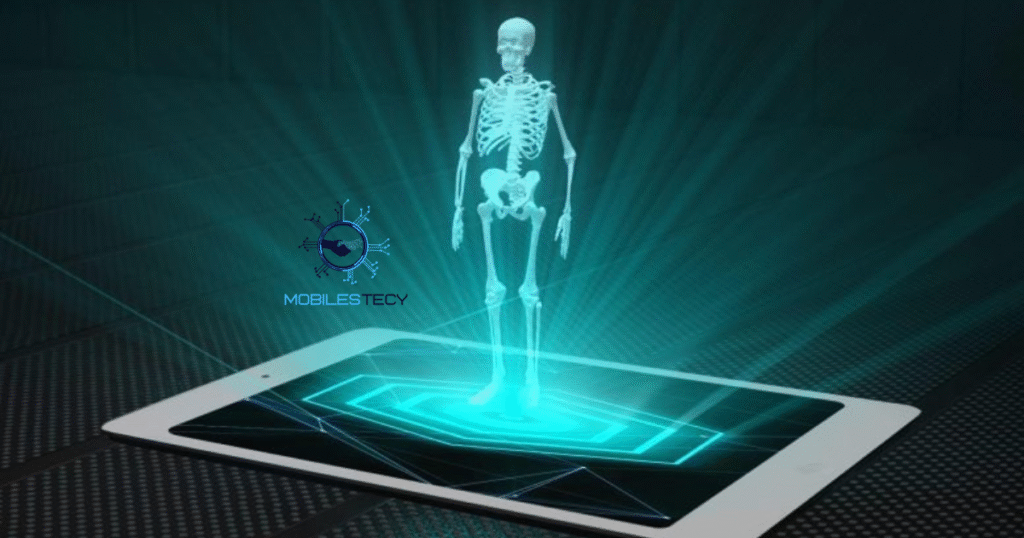

Holographic projection technology creates three-dimensional images appearing to float freely. It uses specialized equipment to control light reflections and visual depth perception. Through precise alignment, projected images resemble solid objects suspended in space. This illusion relies on advanced optics and reflective surfaces positioned strategically. High-resolution video content enhances clarity, realism, and audience visual engagement.
Many holographic setups utilize transparent film screens angled to reflect projected visuals. This creates a realistic three-dimensional appearance viewable from multiple directions. Proper lighting is crucial to hide projection sources and maintain illusion. Darkened environments often improve depth perception and display contrast intensity. With fine calibration, holographic visuals appear smoother and more naturally integrated.
Advanced holographic systems are scalable for small displays or large theatrical presentations. Portable units support retail advertising, while massive installations enhance stage performances. The flexibility of these systems encourages creative experimentation across various industries. As technology improves, holographic images gain sharper detail and more realistic depth. Future developments may allow 3D projection viewable without reflective surfaces entirely.
- Holographic technology creates three-dimensional visuals appearing suspended without physical screens.
- Advanced projection systems use lasers, mirrors, and transparent films for realistic 3D projection.
- Proper lighting conditions enhance hologram clarity and improve depth perception significantly.
Laser-Based Holography
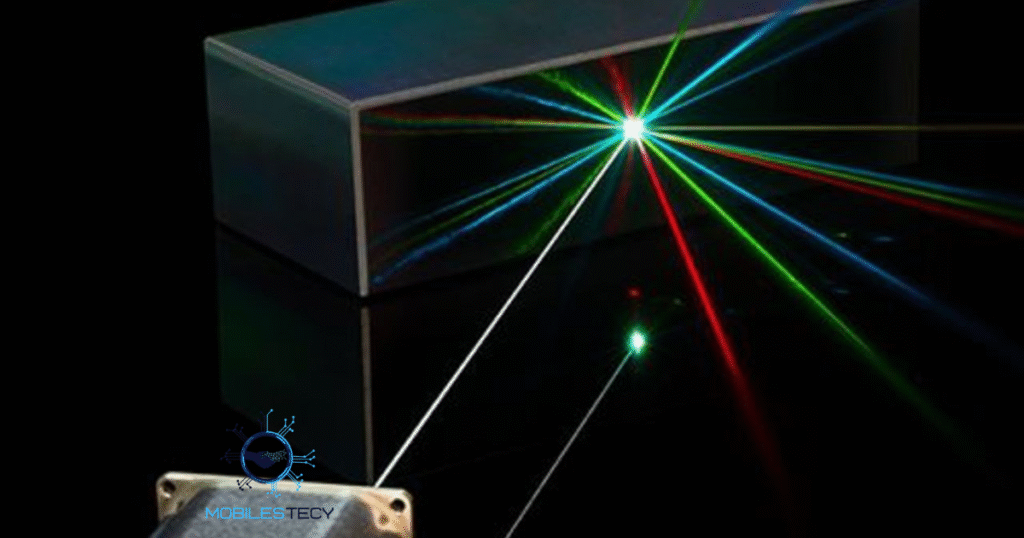
Laser-based holography records light interference patterns from illuminated physical objects realistically. This process captures depth information invisible in traditional two-dimensional photographic methods. When illuminated again, holographic plates recreate realistic three-dimensional visual appearances convincingly. Laser coherence ensures accurate wave reconstruction producing detailed and stable holographic images.
Holographic recording requires controlled environments to minimize vibrations and light interference. High-quality lasers maintain consistent wavelengths for precise hologram creation outcomes reliably. Material sensitivity affects clarity, brightness, and long-term 3D projection durability significantly overall. Researchers continuously enhance holographic stability through advanced optical material developments worldwide.
Digital Light Manipulation Techniques
Digital holography uses algorithms to calculate interference patterns representing visual data. These patterns instruct light modulators to shape beams into three-dimensional forms. Spatial light modulators adjust pixel-level brightness for accurate depth reproduction. The result appears like genuine objects existing in a shared viewing space. This process allows holograms to change dynamically in real-time presentations.
High-performance processors are essential for generating complex holographic visual calculations. More computing power improves movement smoothness and reduces distortion artifacts. Graphic engines integrate animation models, lighting effects, and shading algorithms. This integration ensures holographic elements appear natural and visually appealing. Continued advancements enable larger holograms with minimal delay or flickering.
Software customization allows holograms to match specific branding or thematic needs. Designers can modify color tones, animation speed, and motion behavior easily. Interactive 3D projection respond to gesture sensors or voice-based navigation systems. Such 3D projection create immersive environments suitable for learning or entertainment showcases. These features make digital holography highly adaptable and future-forward technology.
Holographic Projection Films
Projection films reflect images to create floating holographic visuals on stage. These films are transparent allowing audiences to see through projected illusion. Proper angle placement ensures visuals appear suspended without noticeable supporting structures. Lighting control hides film edges maintaining convincing three-dimensional presentation quality effectively.
High-resolution projectors supply crisp visuals improving depth perception and detail realism. Film durability allows repeated use during performances, exhibitions, and promotional displays. Large installations require careful calibration to avoid distortion or visual misalignment. Holographic projection films remain popular due to cost effectiveness and scalability.
Volumetric Display Methods
Volumetric displays create holograms by forming light points in physical space. Some systems use rotating LED arrays producing perceived three-dimensional motion effects. Others rely on mist or fog screens capturing projected light for depth. These methods generate tangible volumetric visuals visible without specialized eyewear assistance.
Volumetric displays offer strong immersion but currently limited in size capability. Higher resolution requires faster processing and more precise light control mechanisms. Despite limitations, volumetric holograms are improving through innovative engineering designs globally. Future developments may enable room-sized holographic environments for interactive experiences soon.
Applications of Modern 3D Projection
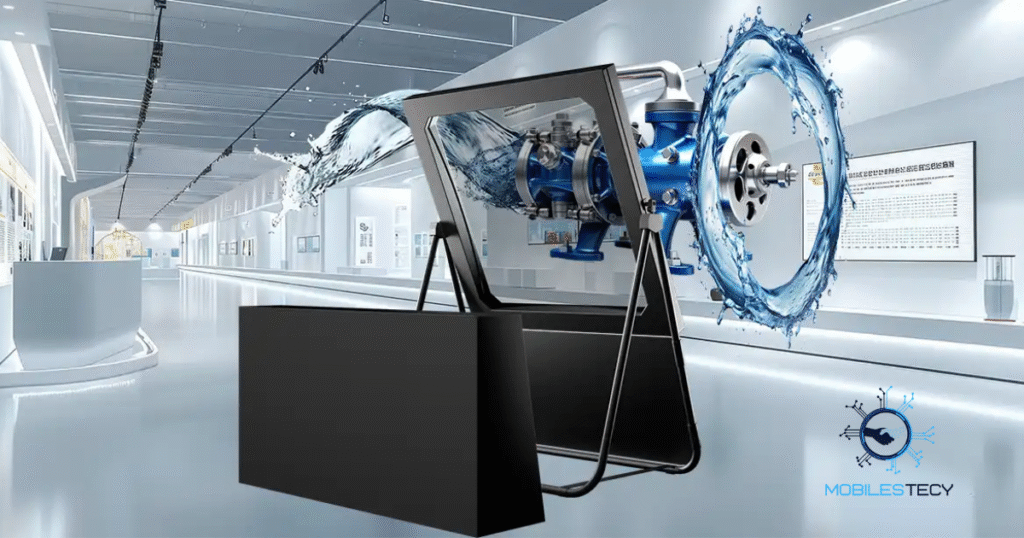

Entertainment industries widely use holograms for concerts, events, and artistic exhibitions. Virtual performers can appear onstage even after their physical absence. This creates memorable experiences that blend creativity, nostalgia, and technology. Audiences appreciate the lifelike presence displayed with dynamic motion effects. Holographic concerts demonstrate powerful emotional and visual impact worldwide.
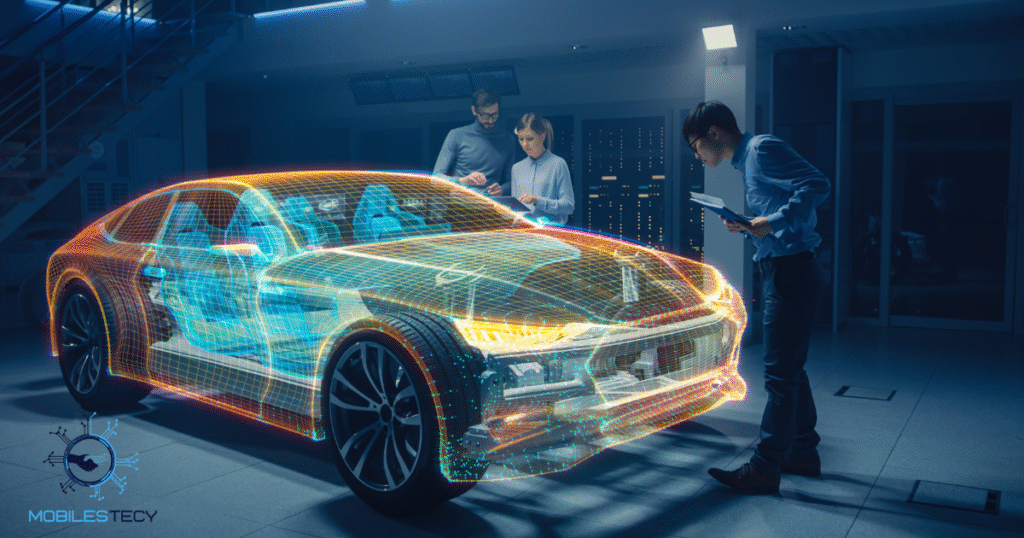
In business settings, holograms assist product launches and executive presentations impressively. They provide visual clarity while reducing travel requirements for remote communication. Companies use 3D projection to showcase prototypes before manufacturing begins. This allows real-time feedback and collaborative design discussions easily. Corporate events become engaging when holographic hosts guide presentations smoothly.
Educational institutions employ 3D projection to illustrate scientific models and historical figures. Students benefit from visual learning that strengthens understanding and retention. Medical training uses holographic anatomy projections for safe, repeatable practice. Such methods improve comprehension and reduce reliance on physical specimens. Thus, holographic applications support education, research, and professional development.
- Volumetric displays form images using light points floating directly in air.
- Holographic concerts allow virtual performers to appear live before physical audiences.
- Businesses use holograms for product demonstrations and high-impact presentation experiences.
Mixed Reality 3D Projection
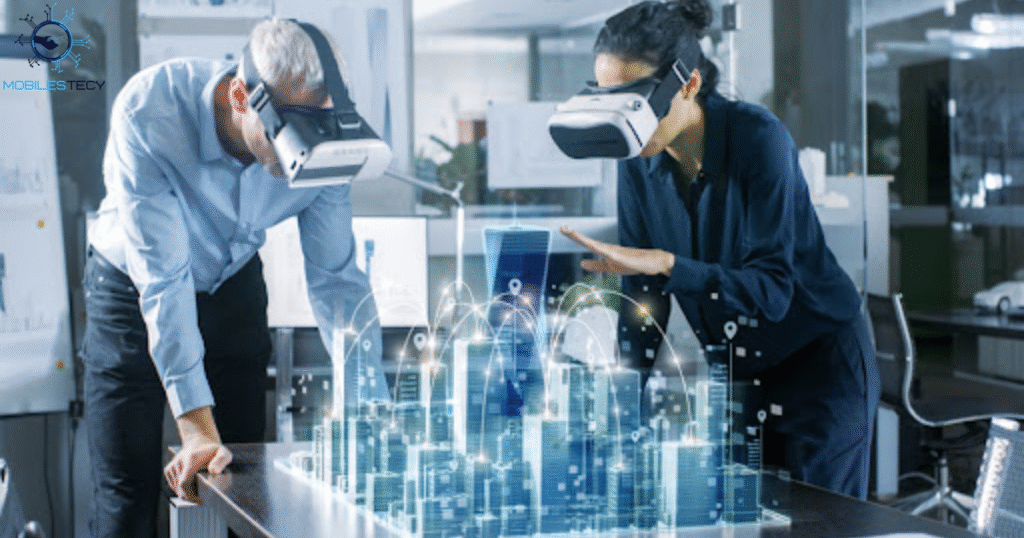

Mixed reality holograms appear through headsets blending digital and physical environments. Users perceive holographic objects integrated naturally within their real surroundings seamlessly. Depth sensors track spatial movement enabling responsive 3D projection positioning changes accurately. This creates immersive experiences helpful for training, simulation, and collaborative work.
Mixed reality holograms assist medical learning, architectural planning, and industrial maintenance. They allow users to interact with virtual models through gestures directly. This interaction increases understanding, retention, and task accuracy significantly for learners. Growing adoption suggests mixed reality 3D projection will expand professional training solutions.
- Educational institutions apply holograms to visualize complex scientific models clearly.
- Medical training benefits from holographic anatomy views for repeated practice sessions.
- Mixed reality headsets integrate digital 3D projection with actual surroundings seamlessly.
- Advancements in computing power improve hologram stability, motion smoothness, and resolution.
- Future holography aims to eliminate screens entirely for free-floating visual interaction.
Faq’s
What is holographic projection technology and how does it create images?
It manipulates light reflections to produce three dimensional visuals appearing suspended. This process uses projectors, reflective films, and precise environmental lighting conditions.
How do holographic films enhance visual clarity during projection displays?
They reflect projected images cleanly while remaining transparent to viewers. Proper angle placement ensures convincing three dimensional illusions during performances.
What role do lasers play in traditional 3D projection creation techniques?
Lasers generate coherent light essential for accurate interference pattern recording. Stable wavelengths allow detailed and durable three dimensional holographic imaging.
Where are holographic displays commonly used in modern industry today?
They appear in entertainment, retail marketing, education, communication, and medical training. Their immersive visual impact enhances engagement and message retention effectively.
Can holographic technology become more advanced and widely accessible in future?
Yes, ongoing research continuously improves projection quality and system affordability. Future developments may enable large, free floating holograms without supporting surfaces.
Conclusion
Holographic technology continues evolving, transforming digital communication and visual presentation methods. It bridges physical and virtual environments with captivating three dimensional visual experiences. Researchers enhance projection clarity, depth, and realism through ongoing scientific innovation. As systems improve, holograms become more accessible for public and professional use. This growth encourages widespread adoption across industry, education, and entertainment sectors.
Holographic projection supports immersive interaction, enhancing communication effectiveness and emotional engagement. By visualizing complex ideas, 3D projection simplify learning and conceptual understanding significantly. Businesses use holograms for product showcases, remote presentations, and audience-focused events. Entertainment industries benefit through virtual performances and interactive stage experiences. These applications demonstrate holography’s potential to reshape communication and creative expression.
As technology advances, holographic displays may eventually project freely in open air. Future innovations could eliminate reliance on reflective films or head-mounted devices. Improved processing power will deliver smoother motion and greater visual depth. Growing research investment suggests holography will expand in mainstream accessibility. Ultimately, holographic technology promises more immersive communication in future digital society.
Read more latest Articles on Mobilestecy.com








